Prostate cancer occurs when prostate cells grow uncontrollably. Early detection is key. Symptoms include urination problems, pain, or blood in urine. Diagnosis uses PSA tests, exams, and biopsy. Treatments include surgery, radiation, hormone therapy and newer therapies.
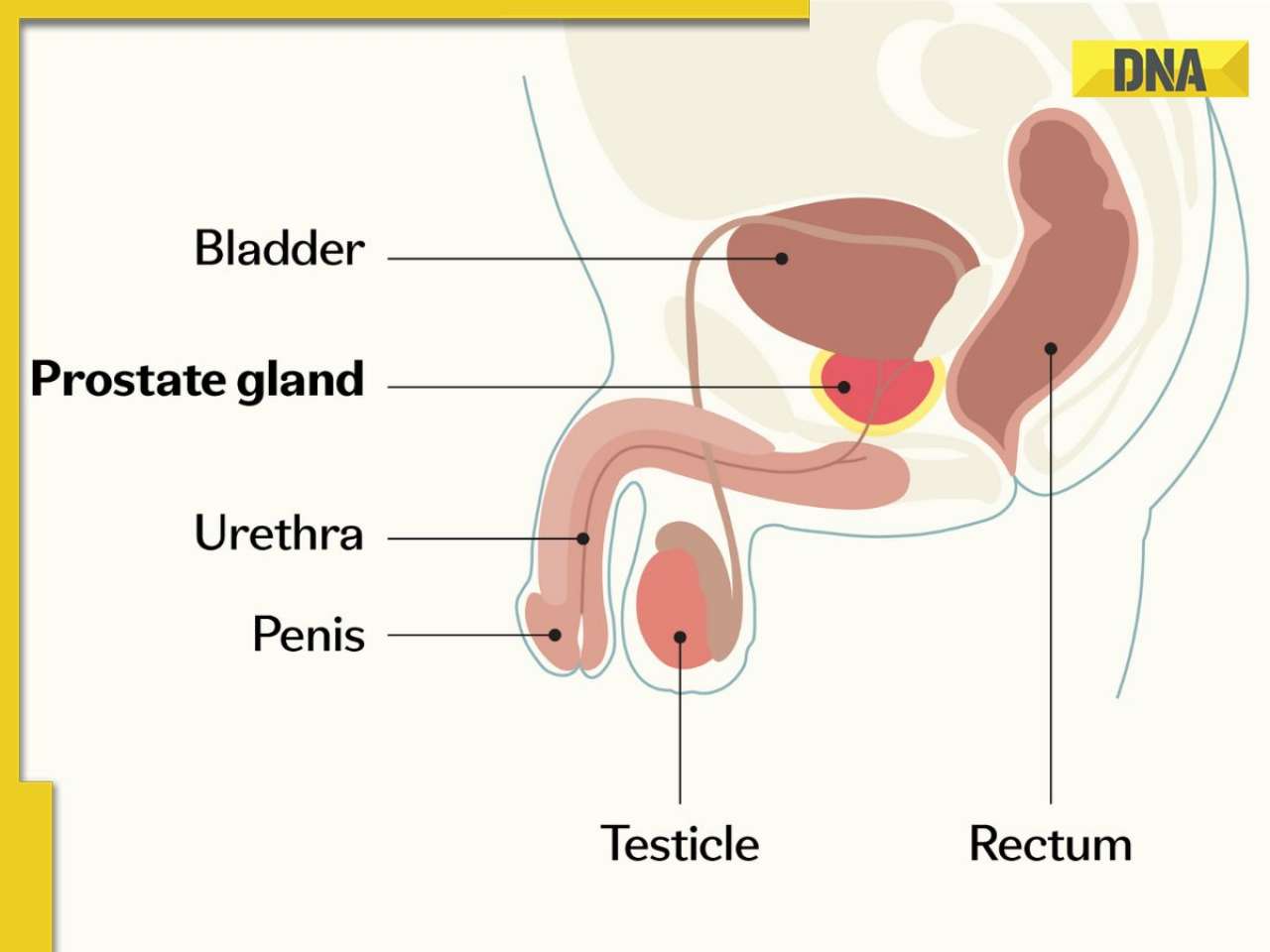
The prostate is a small gland in men, located below the bladder. It aids in the production of sperm fluid. When certain cells in this gland begin to grow out of control and develop into a tumour, prostate cancer results. Cancer can occasionally spread to other body parts. Early detection is crucial because the likelihood of a successful course of treatment increases with early detection.
Symptoms to watch for:
Prostate cancer frequently shows no symptoms in its early stages, which is why routine examinations are crucial. When symptoms do manifest, they could include difficulty urinating, a weak urine flow, or the sensation that the bladder is not empty. Additionally, men may notice blood in their urine or semen or need to urinate more frequently, particularly at night. Pain in the hips, pelvis, or lower back, as well as erection problems or painful ejaculation, are additional potential symptoms. Additionally, unexplained weight loss, exhaustion, or bone pain may occur if the cancer spreads.
How Doctors diagnose prostate cancer:
A prostate cancer diagnosis is made by a combination of the following tests, which doctors use. With the help of the PSA blood test, the level of a protein that might be elevated due to cancer is determined. The doctor performs a digital rectal examination (DRE) to identify lumps by palpating the prostate via the rectum. MRI or ultrasound imaging can reveal areas of interest, and a biopsy takes a small tissue piece to check the cancer. Drs. weigh the scores and stages to determine the degree of the cancer and thus the most effective treatment plan.
Treatment options:
The age, health and stage of the cancer determine the treatment. Doctors may opt for active surveillance (periodic examinations) for the slow-growing cancer. Among the other treatments are prostatectomy, radiation therapy, hormone therapy, chemotherapy and advanced cancer treatments for metastasis. There are also new treatments such as targeted therapy and immunotherapy.
Disclaimer : This story is auto aggregated by a computer programme and has not been created or edited by DOWNTHENEWS. Publisher: dnaindia.com